- Print
- PDF
By signing a XML file using a digital certificate, you allow the recipient to verify both the origin and the integrity of the file. This means that the recipient is able to verify that the XML is the original and has not been changed after it was created.
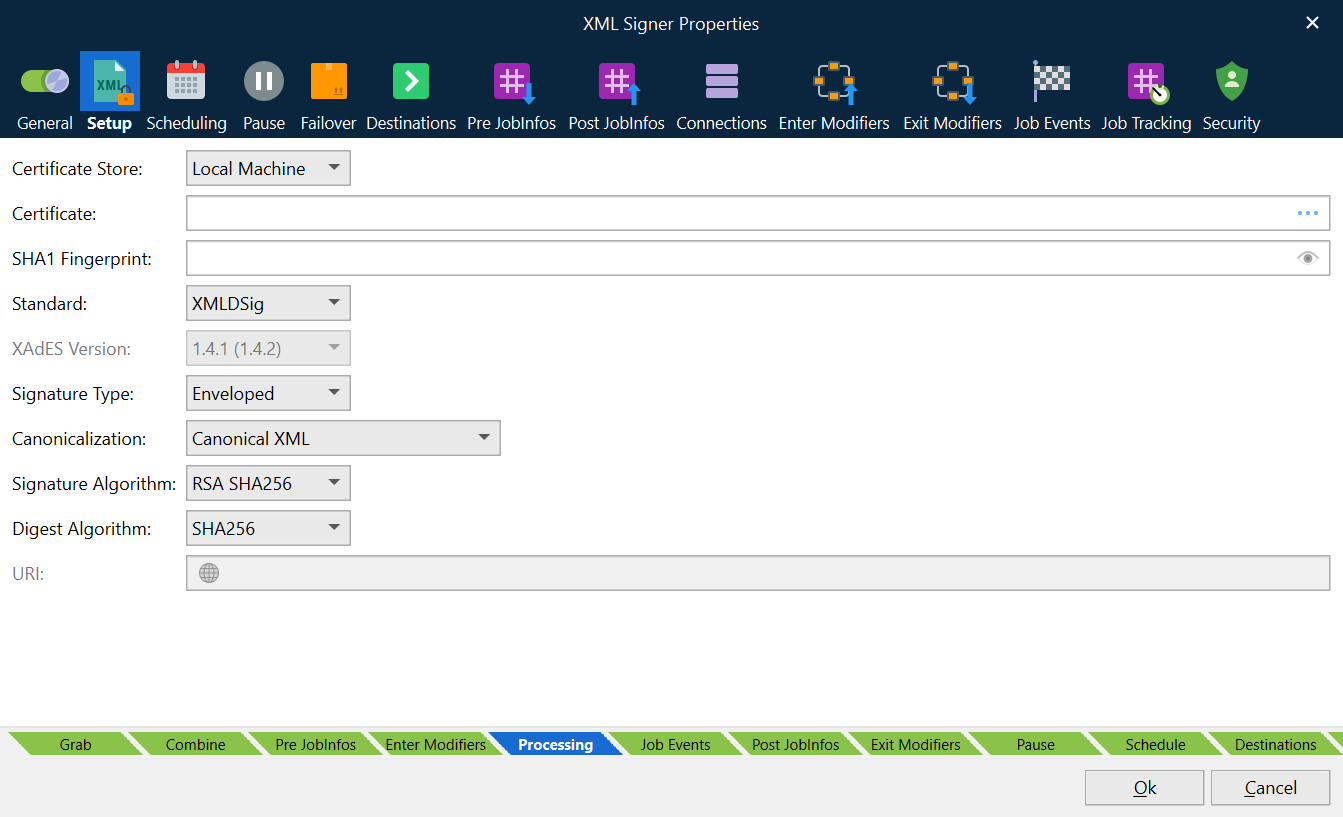
Certificate Store
Select whether the certificate is located on the Local Machine or the Current User account.
Certificate
In order to sign the PDF using a digital signature, you must have a valid and appropriate certificate installed for the user account that the Lasernet service is running under.
SHA1 Fingerprint
Used to verify that the signed file is unaltered. The checksum is created before the file is transmitted, and then once again when it reaches its destination.
Standard
XML Digital Signatures (XMLDSIG) or XML Advanced Electronic Signature (XAdES) are supported for signing and validating.
XAdES Version
Set version for XML Advanced Electronic Signature (XAdES).
1.2.2
1.3.2
1.4.1 (1.4.2)
Signature Type
Enveloping signature is over content found within an object element of the signature itself. The object (or its content) is identified via a reference (via a URI fragment identifier or transform).
Enveloped signature is over the XML content that contains the signature as an element. The content provides the root XML document element.
Detached signature must be placed in a separate file next to the XML document
Note
The signature data is placed in JobData and overwrites the original XML contents. XML data must be stored in a separate JobInfo or forwarded to an additional destination before signing.
Canonicalization
Canonical XML specifies a standard serialization of XML that, when applied to a subdocument, includes the subdocument's ancestor context including all of the namespace declarations and attributes in the xml: namespace:
Canonical XML
Canonical XML with comments
Canonical XML 1.1
Canonical XML 1.1 with comments
Exclusive
Exclusive with comments
Minimal
Signature Algorithms
Specifies the hash to protect from tampering:
DSS
RSA MD5
RSA SHA1
RSA SHA224
RSA SHA256
RSA SHA384
RSA SHA512
ECDSA SHA1
ECDSA SHA224
ECDSA SHA256
ECDSA SHA384
ECDSA SHA512
Digest Algorithms
Specifies the hash algorithm before applying the hash.
MD5
SHA1
SHA224
SHA256
URI
Sets the Uniform Resource Identifier.

