- Print
- PDF
After you add a Form Engine to your project (see the Form Engine chapter in the Lasernet Developer guide), you are ready to start creating forms. To create a form, follow these steps:
Select the Forms developer tool in the main window of Lasernet Developer.
Select your Form Engine on the left-side list view, and then click the Add button in the toolbar.
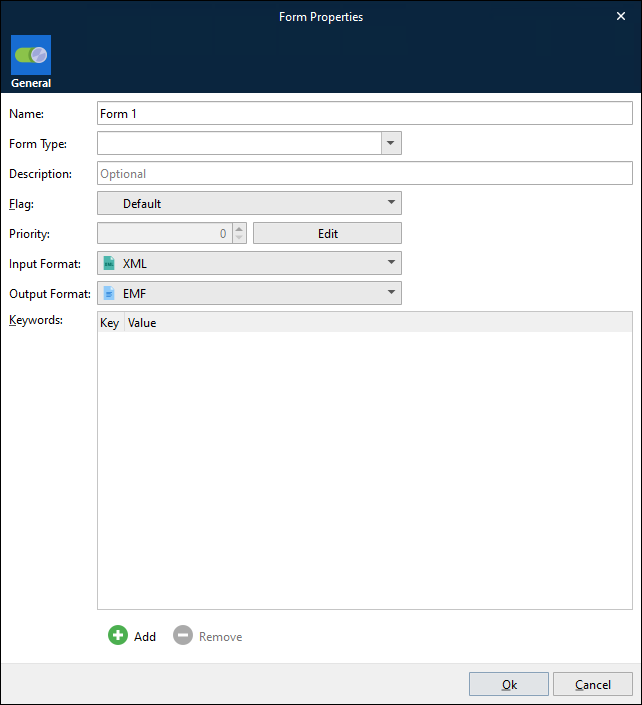
Provide a name and a description for your new form in the Form Properties dialog, and then select the appropriate input format and output format. Click Ok to create the form.
Note
It is important that you choose the correct Input Format and Output Format for your new form. The format settings define the input type expected by Lasernet (CSV, EDI, JSON, Text, XLS or XML) and the output format it should deliver report contents as: CSV, EDI, EMF, PDF, TIFF, XHTML, XML, Rich Text (DOCX, PDF, and XHTML), XLSX, or DataSet. You cannot change the properties for the form once it has been created, but it is possible to add new sheets and remove old ones to change the output.
The following sections of this page contain more information about input types and output types.
If you are working with text-format input data: You might need to set up input job splitting, set up job combining, or both.
To start editing your new form, double-click it, or right-click it then select Edit from the context menu.
If necessary, specify the regional profiles that the form will use for incoming data.
If necessary, add form criteria to specify what data the new form is suitable for.
Lasernet creates a blank sheet (Sheet 1) in your new form. Appropriately change the sheet's options to suit project requirements.
If applicable, identify the area in the input data that contains line item data.
Note
This step is applicable to text input data only.
If relevant, identify the line items in the input data so that Lasernet can add them to output documents.
Depending on the Output type of a sheet, create the sheet’s structure. For some sheets you must create the structure of the output before you design the sheet’s output.
Create the sheet design. See the pages in the Design a Form part of this guide.
If necessary, add more sheets to the form.
Input Formats
The following input formats are available:
Text
XML
JSON
CSV
EDI
XLS(X)
DataSet (XML)
Note
If you select an Output Format that requires input in DataSet format, the form’s Input Format will automatically change to DataSet.
JSON Input
It is possible to work with forms based on the JSON input, which is derived from a grab file exported by any system on any platform. Handling and processing the JSON input form type in Lasernet Form Editor is similar to the operations with the XML input form type.
Note
Compared to XPath, JPath provides limited operations for accessing parent or sibling nodes.
CSV Input
Input files in CSV format are automatically converted to XML. Handling and processing CSV input in Lasernet Form Editor is similar to XML input.
When a CSV grab file is opened, it is automatically converted to XML.
EDI Input
EDI-formatted input files are automatically converted to XML. Handling and processing EDI files in Lasernet Form Editor is similar to XML input.
When an EDI grab file is opened, it is automatically converted to XML.
XSL(X) Input
XLS formatted input files are automatically converted to XML. Handling and processing XLS files in Lasernet Form Editor is similar to XML input.
When an XLS grab file is opened, it is automatically converted to XML.
Spreadsheets created in Microsoft Excel 2007 or newer are supported. Microsoft Excel does not have to be installed to convert Excel into XML.
See Configure XLS(X) Data Input.
Data Fields from Spreadsheets
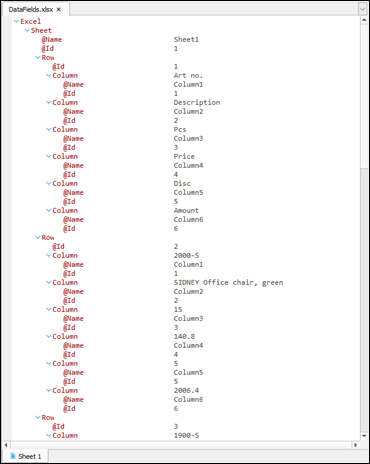
Rows and columns on all sheets are extracted and saved into the XML structure.
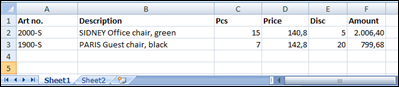
Above is an example of the first sheet, named Sheet1, containing a header and two rows.
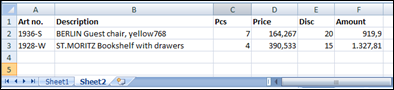
Above is an example of a second sheet, named Sheet2, containing a header and two rows.
The final result is:
An XML file containing an
<Excel>root nodeA child for each sheet named
<Sheet>with attributes for@Id= Sheet index,@Name= Sheet nameSub-node for each row named
<Row>with attribute for@Id= Row indexSub-node for each column named
<Column>with attributes for@Id= Column index,@Name= Header names for elements (if available/selected)
DataSet (XML) Input
A DataSet is XML data whose structure is displayed (in the Form Editor data area) in a database-like way, in which the structure of the XML data is represented by "tables" and "columns". The structure of the data is displayed, rather than the data itself.
The Form Editor is able to do this because DataSet XML contains schema information that describes the data that the XML contains. As a result, a DataSet file can specify the tables and columns that the data contains, and can specify the data type of each column (Boolean, integer, decimal, string, datetime, or binary).
Because DataSet input contains this schema information, it is considered a distinct input data type to general XML.
Rich-text-based DOCX, PDF, and XHTML output and XLSX output require input data in DataSet format.
Output Formats
The following output formats are available:
CSV
EDI
EMF
PDF
PDF/UA
TIFF
XHTML
XML
Rich Text (DOCX, PDF, and XHTML)
XLSX
JSON
DataSet
PDF Form (Filled)
The output format that you choose determines the output format of the first sheet (Sheet1) that Lasernet adds to the new form.
Rich-text-based DOCX, PDF, and XHTML output and XLSX output require input data in DataSet format. Other output types (including the EMF-based PDF output) require text, JSON, or XML format input data (or data in a format that Lasernet can convert to XML, such as CSV).
Underlying Output Formats
Although Lasernet supports all the output formats listed above, many of them have the same underlying format. When Lasernet generates an output document, it first generates the document in the relevant underlying format, and then it converts that document into the form or sheet’s selected output format.
The format named at the start of each bold row in the Output Format list is the underlying format for the output formats listed below it. For example, the underlying format for CSV output documents is XML (Extensible Markup Language).
.png)
Some output formats have more than one possible underlying format. For example, PDF output can be Enhanced Metafile (EMF) based or rich-text based. For formats like these (such as PDF), your selection from the menu above determines which underlying format is used. The first PDF item in the menu creates documents whose underlying format is EMF; the second PDF item creates documents whose underlying format is rich text.
Your experience of designing the form in the Form Editor will differ depending on the underlying format. For PDF, this is because the page-based form creation tools provided for EMF-based documents differ from the tools provided for creating rich text documents (which have a page design editor that is similar to Microsoft Word).
Because some output types have more than one possible underlying format, this guide uses terminology like “EMF-based” where necessary, to indicate which of an output format’s multiple possible underlying formats a particular section of Form Editor documentation is about.
PDF Output (EMF-Based)
PDF output converts EMF data to PDF format. The Form Engine retrieves data from the input grab file, processes it, maps it to fields in the output file, and then automatically converts the result to PDF.
Sheets whose output format is PDF have specific sheet options. See Configure PDF Output.
Note
The EMF-based PDF output type is distinct from the rich-text based other PDF output type.
However, both PDF output types have the same PDF-specific additional sheet options.
Note
This output type has a prespecified page-based structure. So, for this type of output you do not need to create a sheet structure; instead, you can proceed straight to adding text, input data, and other elements to the form design.
PDF/UA Output
PDF/UA output converts EMF data to PDF/UA format. The Form Engine retrieves data from the input grab file, processes it, maps it to fields in the output file, and then automatically converts the result to a PDF/UA-compliant PDF document.
PDF/UA stands for Portable Document Format / Universal Accessibility. PDF/UA-compliant documents make their content readable by assistive technologies (such as screen readers)
Sheets whose output format is PDF/UA have specific sheet options. For more information about PDF/UA and about the sheet options for PDF/UA sheets, see Configure PDF/UA Output.
Note
PDF/UA support applies only to documents whose underlying format in Lasernet is EMF. PDF/UA support for RTF-based PDF documents is not available.
Note
This output type has a prespecified page-based structure. So, for this type of output you do not need to create a sheet structure; instead, you can proceed straight to adding text, input data, and other elements to the form design.
XML Output
The XML tab is designed to edit content of the XML output in the XML source editing mode.
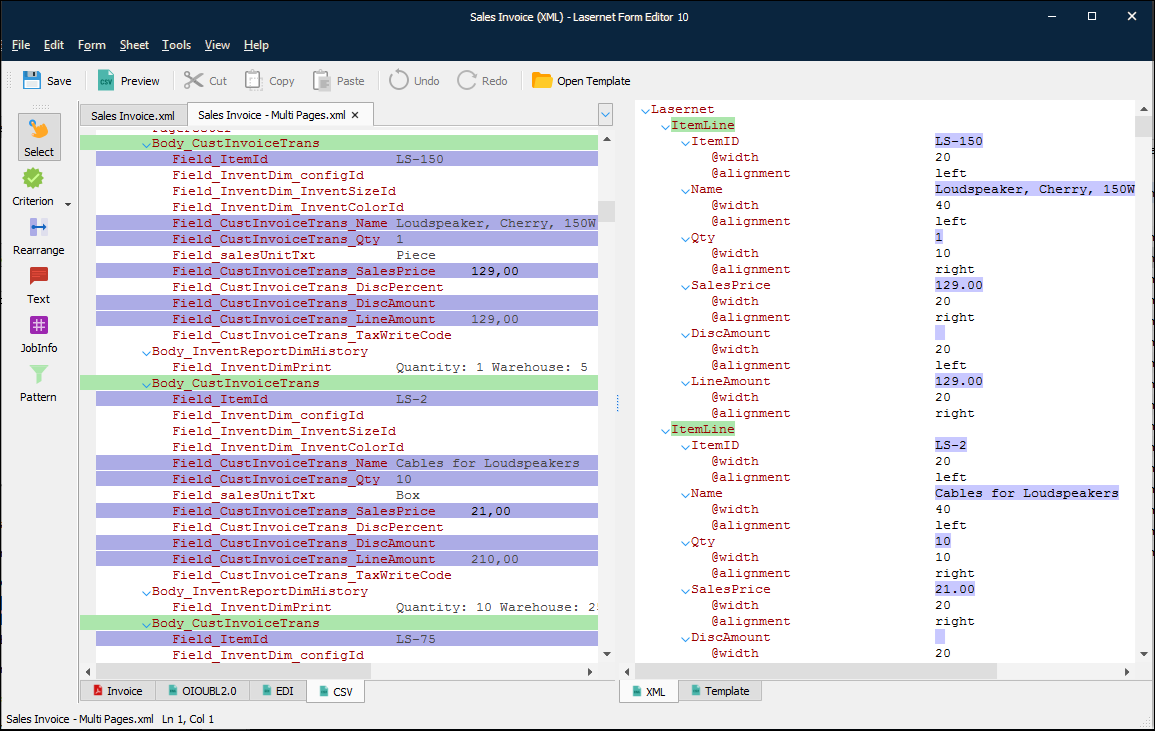
Note
For sheets that have this output type, you must specify the sheet's structure before you create the sheet’s output design. See the appropriate part of Create the Sheet Structure.
Sheets whose output format is XML have specific sheet options. See Configure XML Data Output.
JSON Output
Creating JSON output data is similar to creating XML output data.
Note
For sheets that have this output type, you must specify the sheet's structure before you create the sheet’s output design. See the appropriate part of Create the Sheet Structure.
Sheets whose output format is JSON have specific sheet options. See Configure JSON Output.
Rich-Text-Based DOCX, PDF, and XHTML Output
Lasernet can create DOCX, PDF, or XHTML output content that is based on a rich-text format page design. The Form Engine retrieves data from the input file, processes it, adds defined data fields to the output along with static elements and text added by a user (while they were modifying the form output design in the Form Editor), and then converts the result to DOCX, PDF, or XHTML.
As an input, the DataSet format is always used.
When you create a form design for a rich-text-based output format such as DOCX, you use tools that look and work similarly to Microsoft Word. You create your form design directly on the single page on the right-hand side of the Form Editor window.
Sheets whose output format is rich-text-based have specific sheet options. See:
See the XHTML Image Translation section in the XHTML (XML-based) output area of Add Images to a Sheet.
Note
This output type has a single-page based structure. So, for this type of output you do not need to create a sheet structure; instead, you can proceed straight to adding text, input data, and other elements to the form design.
Note
As described elsewhere on this page, instead of being rich-text-based, PDF output can be EMF-based, and XHTML output can be XML-based.
XHTML (XML-Based) Output
On the Template tab of the Form Editor, you can use commands in the right-click menu and tools on the Property bar (see the following picture) to create and format the output. These features are similar to those in Microsoft Word, but are not described in this manual.
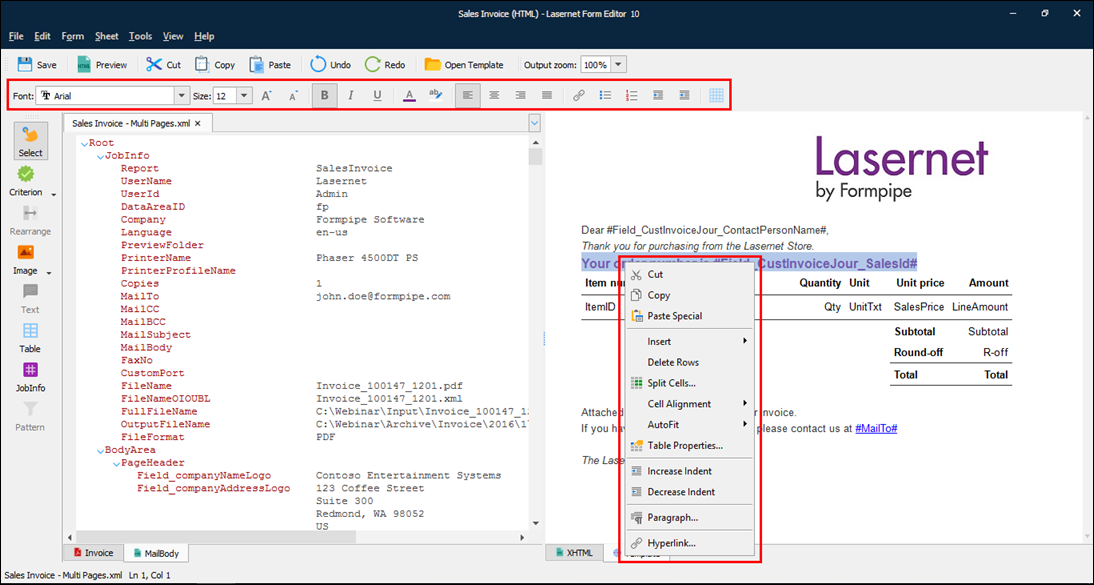
Note
For sheets that have this output type, you must specify the sheet's structure before you create the sheet’s output design. See the appropriate part of Create the Sheet Structure.
Note
Lasernet’s tools for creating XML-based XHTML output provide limited formatting features, when compared to the tools provided for creating rich-text-based XHTML output. Lasernet’s XML-based XHTML output capability is deprecated and will not receive any future updates.
EDI Output
To create EDI output data, the Form Engine retrieves data from the input grab file, processes it, maps it to fields in the output, and automatically converts the result to EDI.
The XML tab is designed to edit the content of the EDI output data in the XML source editing mode. The Template tab is designed to create, edit, and preview the structure of the EDI output data.
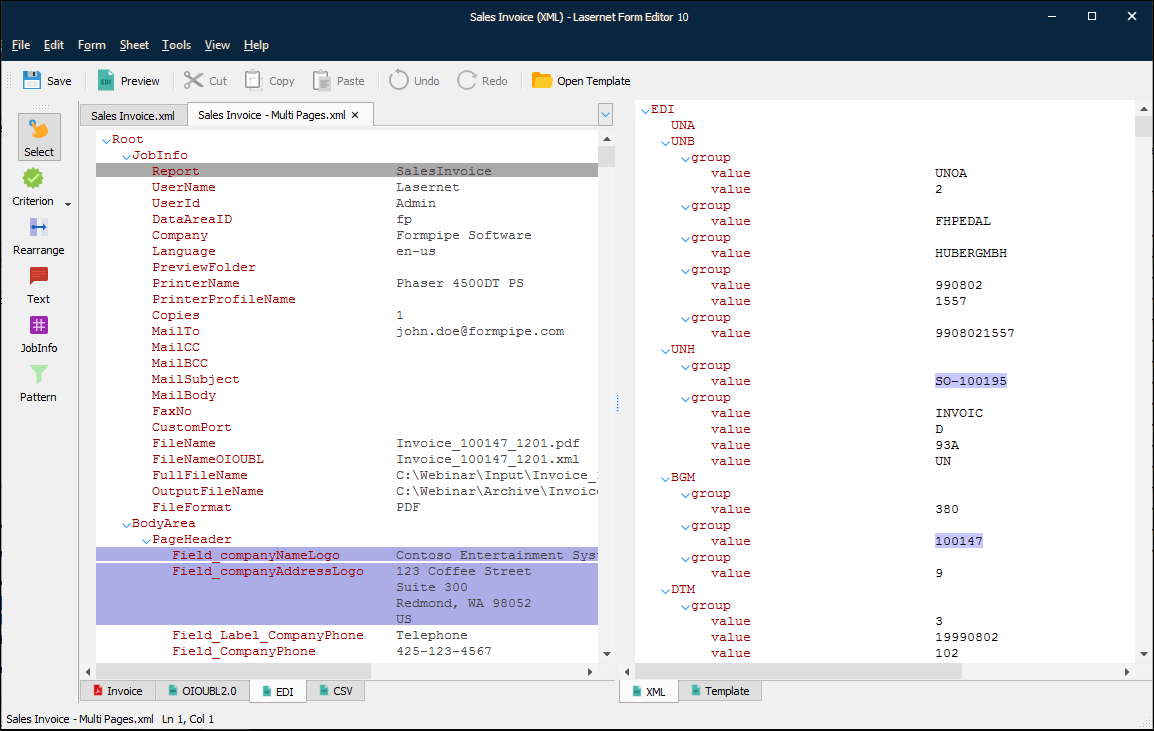
Note
For sheets that have this output type, you must specify the sheet's structure before you create the sheet’s output design. See the appropriate part of Create the Sheet Structure.
Sheets whose output format is EDI have specific sheet options. See Configure EDI Output.
DataSet Output
DataSet output is data in XML format with an embedded XML Schema Definition (XSD). The Form Engine retrieves data from the input grab file, processes it and maps it to fields in the output.
In Lasernet, a DataSet output file can be used as an input for forms that create output in the Rich Text and Spreadsheet output formats.
In summary, creating DataSet output involves the following process:
Add a grab file to the form.
Add a pattern to the input data.
Add rearranges if required.
Use the Format Category list (on the Format tab of the rearrange properties dialog) to set a format category for numeric, date or time values for a node.
Create an output structure for the DataSet output.
Properties for DataSet Forms
The DataSet output format has the same properties as XML does, except for DTD Declaration which is not present for the DataSet output format.
XLSX Spreadsheet Output
Lasernet can create output files in XLSX format. The Form Engine retrieves data from the input file, processes it, and adds defined fields to the output along with static elements and text added by a user while modifying the output in the Editor.
As an input, the DataSet format is always used.
Lasernet uses a Microsoft-style interface to design XLSX formatted output.
Note
For sheets that have this output type, you must specify the sheet's structure before you create the sheet’s output design. See the appropriate part of Create the Sheet Structure.
Sheets whose output format is XLSX have specific sheet options. See Configure XLSX Output.
TIFF
TIFF output converts EMF data to TIFF format. The Form Engine retrieves data from the input grab file, processes it, maps it to fields in the output file, and automatically converts the result to TIFF.
Note
This output type has a prespecified page-based structure. So, for this type of output you do not need to create a sheet structure; instead, you can proceed straight to adding text, input data, and other elements to the form design.
Sheets whose output format is TIFF have specific sheet options. See Configure TIFF Output.
CSV Output
To create CSV output, the Form Engine retrieves data from the input grab file, processes it, maps it to fields in the output, and automatically converts the result to CSV.
Note
For sheets that have this output type, you must specify the sheet's structure before you create the sheet’s output design. See the appropriate part of Create the Sheet Structure.
Sheets whose output format is CSV have specific sheet options. See Configure CSV Output.
EMF Output
Sheets whose output format is EMF have specific sheet options. See Configure EMF Output.
PDF Form (Filled)
PDF files can contain interactive elements such as text boxes, checkboxes, and combo boxes. The PDF Form (Filled) output is used to manipulate such PDF files. This output is designed to work with interactive elements by filling them with data taken from the form input.
Sheets whose output format is PDF Form (Filled) have specific sheet options. See Configure PDF Form (Filled) Output.
Note
For sheets that have this output type, you must specify the sheet's structure before you create the sheet’s output design. See the appropriate part of Create the Sheet Structure.
XML Input and Output
When creating a new form for handling XML input, XML must be specified as the input format.
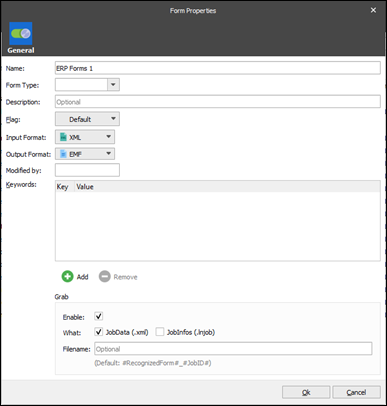
The above form is set to receive XML formatted files and print standard text forms. If XML output is required, the output format would need to be changed to XML.


