- Print
- PDF
Performance Considerations for Lasernet
Several considerations can be taken into account in relation to performance, particularly with reference to the data source. Any one or all of the following steps can be taken to ensure strong and fast application performance and a stable structure:
Delete tables and fields unused by the Query Wizard.
Test your report with real and sufficient data.
Check your table relations so that you do not get unnecessary data/structure.
Empty ranges or no ranges often cause slow performance, as all the records can be fetched.
Add a field to an index. Fields that do not belong to any index can slow performance because a full table scan is used to find the related record(s). It is recommended that a field be added to an index to avoid a potential full table scan and ensure performance.
If a data source has multiple child data sources at the same level with Fetch mode 1:1, where an inner join is required, consider using a sub-query. It is possible to avoid performance issues and optimize the structure by adding sub-queries to the existing Query (main Query).
A new option for disabling and re-enabling the data sources has been introduced within the Query Wizard. It may be useful when optimizing performance and locating data sources (tables) that cause no output.
To solve the performance issues using Performance indicators, follow these steps:
Activate Performance indicators when optimizing performance for a report.
For more information on Performance indicators, visit this link.
Run the report to a destination (not Lasernet Screen). It is recommended that you use either Email or Fax.
For example, use Fax as the destination and 1234 as the print number.
Locate the part causing slow performance and disable data sources within this part of the Query (for instance, disabling half of the data sources).
Re-run the report and re-check the infolog regarding the part of the structure that was causing slow performance.
Check the table used for the relations and indexes for the tables, which causes slow performance.
Data Source and Size Limits
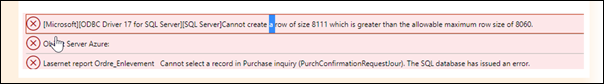
SQL Server has a limit row size of 8060 bytes; if the size exceeds the limit, the following error is displayed:
Error
[Microsoft][ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server][SQL Server]Cannot create a row of size 8111 which is greater than allowable maximum row size of 8060.
The error occurs because a row in SQL Server cannot be larger than 8KB (the size of one page), as rows are not allowed to span pages. This is a basic limit of SQL Server. For more information, read the documentation by Microsoft.
Data contained for all fields within an entity is contained in an SQL table with a maximum storage of 8060 bytes.
More Microsoft documentation regarding this issue can be found here.
For more information, consult this article and read about the solution to this problem.
Another possible error due to SQL Server limitations occurring when the table and joined tables exceed a row size of 8060 bytes is the following:
Error
Cannot select a record in Project invoice (PSAProjInvoiceHeaderTmp). The SQL database has issued an error.
The query operation has exceeded the maximum row size of SQL Server. Please reduce the number of columns or joined tables.
This error can occur when joined tables are sorted using an ORDER BY clause or grouped using a GROUP BY clause. It may also arise in cases involving joins, such as Hash joins.
It may be possible to solve this issue in Lasernet FO Connector by adding sub-queries to the main Query. Each sub-query has an 8060-byte limit, allowing for the retrieval of nearly unlimited data.
An alternative approach is to modify the standard selection within a GROUP BY Query, which ensures that only specified fields are retrieved from SQL Server. This is useful if a single table contains several fields.
It is also advisable to verify whether the result is obtained using ORDER BY or GROUP BY, as this can be changed if necessary. Additionally, the Dynamic Region feature in Lasernet Form Editor can be used to manage ordering or grouping.
How Does the Data Get Selected?
You can see the infolog with the SQL Query in the performance log (if enabled). Selecting the Full value in the Performance indicators dropdown combo box allows you to add a Query statement (SQL statement) to the Infolog once a report is executed.
Grouping, Fetch mode (1:1/1:N) affects how the SQL query is executed.
Fetch mode/Fetch 1:1 creates an SQL statement such as the following:

Fetch mode/Fetch 1:N creates multiple and separate SQL statements, such as the following:



