- Print
- PDF
Used for sending jobs to an FTP, FTPS, or SFTP server.
FTP
Add an FTP Output module to add a connection to an FTP server.
To connect to an FTP server, enter the address of the server into the Host field. Add the server port number into the Port field (default is 21). If a username and password are required, enter them in the corresponding fields (defaults to anonymous logon if no credentials are specified). Click Determine Settings to validate against the specified host and retrieve information for supported ports, transfer modes, protocols, SSL types and Clear Control Channel (active/not active).
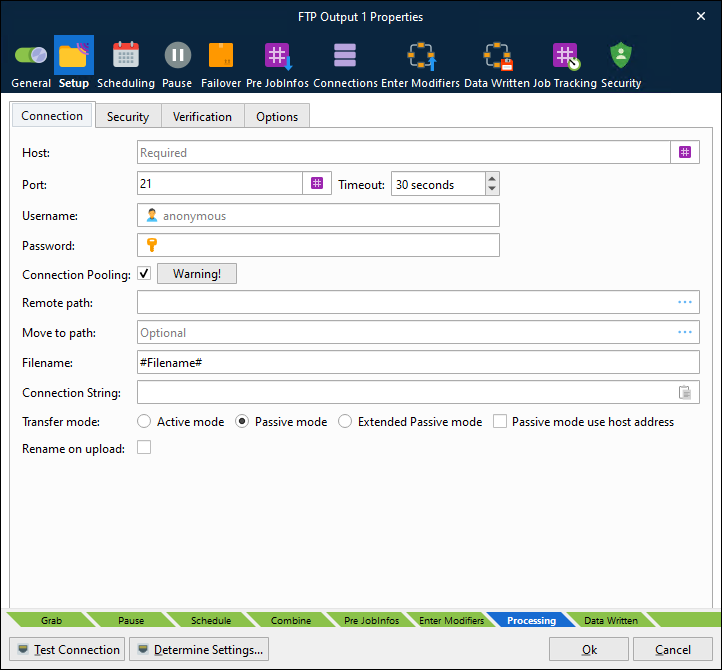
Connection
Host | URL for FTP. Protocol type or remote path should not be included as part of the URL. |
Port | Set port number used by host. Default value is 21. |
Timeout | If the connection cannot be established before the timeout limit it will fail. Default timeout is 30 seconds. |
Username and password | If user authentication is required, enter a username and password, otherwise anonymous logon will be used by default. |
Connection Pooling | Connection pooling is activated by default when adding a new FTP module. It works as a cache to reuse the open connection when other requests to the same FTP server are required. Connection pools enhance performance, since opening and closing an FTP connection is costly and wastes resources.
|
Remote path | The remote path on the FTP server where files need to be uploaded to (if different from the default log in directory of the FTP server). Click the Browse button to select, create or delete a folder on the remote host (if user rights allow it). |
Filename | JobInfo substitution is supported by enclosing the name of the JobInfo, which holds the filename, with hash marks; for example, #Filename#. The value of the JobInfo will then be used as the filename when transferring. Fixed filenames like |
Transfer mode | Active mode, passive mode and extended passive mode are supported. In active mode, the FTP client opens a dynamic port, sends the FTP server the dynamic port number on which it is listening over the control stream and waits for a connection from the FTP server. When the FTP server initiates the data connection to the FTP client, it binds the source port to port 20 on the FTP server. In passive mode, the FTP server opens a dynamic port, sends the FTP client the server's IP address to connect to and the port on which it is listening over the control stream and waits for a connection from the FTP client. In this case, the FTP client binds the source port of the connection to a dynamic port. In extended passive mode, the FTP server operates exactly the same as passive mode, however it only transmits the port number (not broken into high and low bytes) and the client is to assume that it connects to the same IP address that was originally connected to. |
Rename on upload | Option to upload file with a temporary filename and rename when done, to avoid it being picked up before completion. |
FTPS
Add an FTP Output module and enable Auth SSL, Auth TLS,or Implicit SSL/TLS on the Security tab.
Enter the FTPS server’s port number into the Port field on the Connection tab (default is 21).
The Security tab contains the following settings:
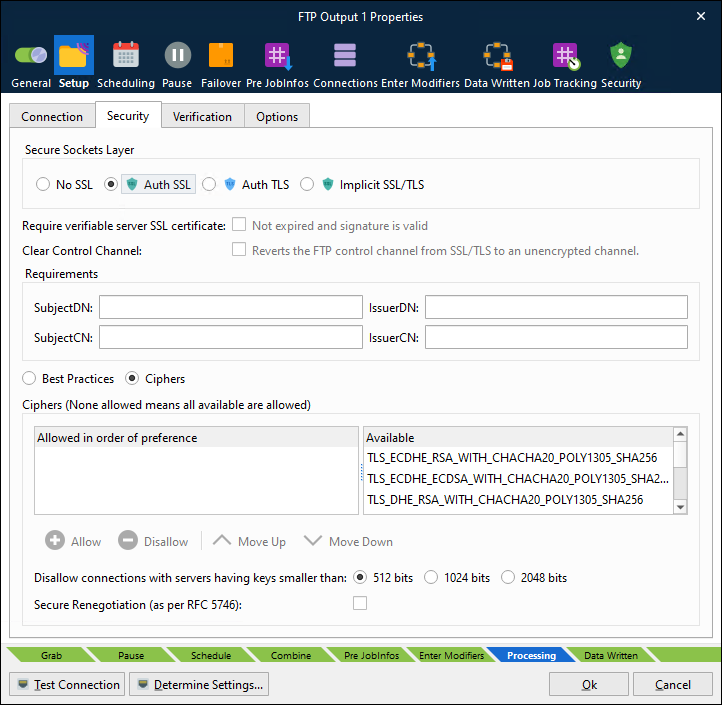
Secure Socket Layer | FTPS (SSL/TLS) is available in two incompatible modes. If using explicit FTPS, the client connects to the normal FTP port and explicitly switches into secure (SSL/TLS) mode with AUTH TLS, whereas Implicit SSL is an older style service that assumes SSL/TLS mode right from the start of the connection (and normally listens on TCP port 990, rather than 21). If a verifiable server SSL certificate is required it must be activated. Ensure that certificate is not expired and the signature is valid. Using Clear Control Channel enables the Firewall to open the correct ports. |
Requirements | SubjectDN: Identifies the DN of the server’s certificate SubjectCN: The certificate owner’s common name IssuerDN: Identifies the CA that issued the certificate IssuerCN: The certificate issuer’s common name |
Best Practices / Ciphers | Click Best Practices to use the default cipher algorithm provided by the server. Click Ciphers to select specific algorithms to allow. Select ciphers in the “available” list then click Allow to move them to the “allowed” list. Their order in the “allowed” list specifies their order of preference; use Move Up and Move Down to change algorithm order. Ciphers provide encryption, authentication, and data integrity checks in file transfer.
You can disallow connections with servers having keys smaller than 512 bits, 1024 bits or 2048 bits. You can choose to Secure Renegotiation (as per RFC 5746). |
Verification
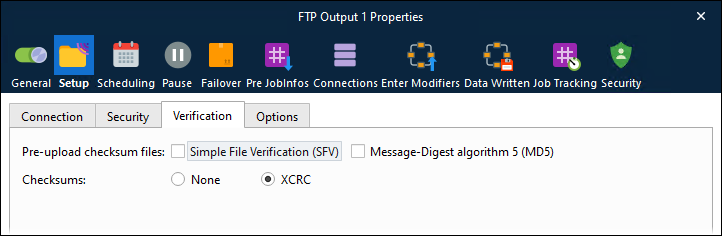
Pre-upload checksum files | A checksum file can be sent first and used for real-time error checking as subsequent files are uploaded. This is a feature or script which the FTP server must support. Lasernet does not currently handle any errors that might occur here. Alternatively, XCRC can be enabled if the server supports it. Files are automatically checked and fixed while uploading, guaranteeing correct delivery. |
Options
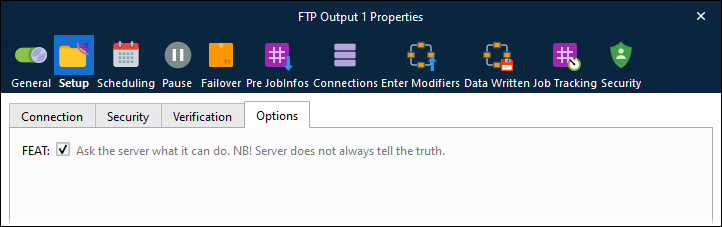
FEAT | Select FEAT if you need to ask the server for additional commands that it supports outside the basic FTP protocol defined in RFC 959. |
SFTP
Add an SFTP Output module to add a connection to an SFTP server. The SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) communicates over a cryptographically protected connection.
Enter the SFTP server’s port number into the Port field on the Connection tab (default is 22).
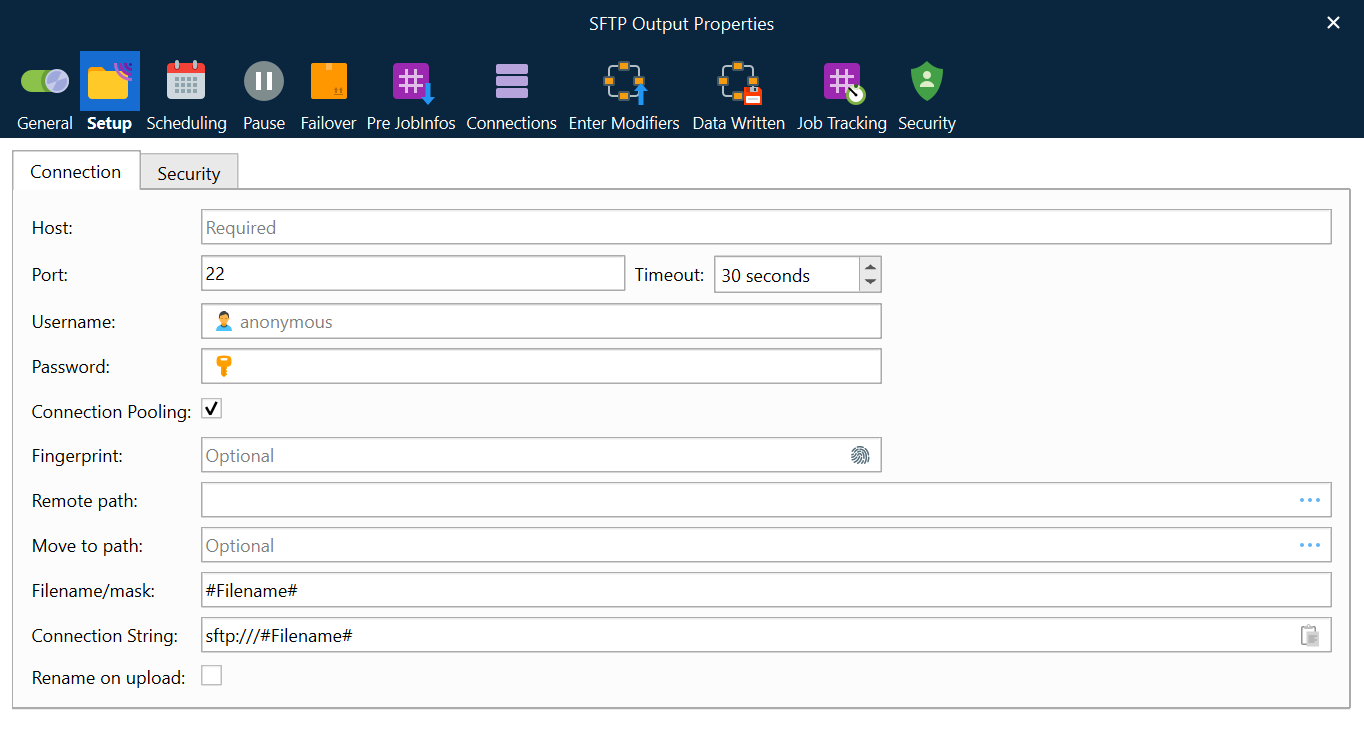
The SFTP protocol has almost identical settings to the FTP protocol, except for the following parameters:
Transfer mode | Not available for SFTP. |
Fingerprint | Before establishing a connection, the SFTP server sends an encrypted fingerprint of its public host keys to ensure that the SFTP connection will be exchanging data with the correct server. Once you have established a connection to an SFTP server and are sure that it is the correct server, you should save the fingerprint information locally. This enables you to check the fingerprint information against the data you have saved every time you establish a new connection to ensure that no one is between you and the server.
|
Security tab | Contains optional Private Key and accompanying Password setting. Contains a Cipher list, which controls the cipher used for the connection. Ciphers provide encryption, authentication, and data integrity checks in file transfer. If no cipher is selected, a cipher is automatically negotiated when establishing the connection. If a cipher is selected but the other party to the connection does not support it, the connection will fail. |
Test Connection
Click Test Connection to check whether Lasernet can successfully connect to the FTP, FTPS, or SFTP server.
JobInfos
The FTP and SFTP Output modules can set the following JobInfos.
Scale | Filename associated with the SFV file. The ".sfv" file extension indicates a checksum file containing 32-bit CRC32 checksums in simple file verification format. |
MD5Filename | Filename associated with the MD5 file. The ".md5" file extension indicates a checksum file containing 128-bit MD5 hashes in md5sum format. |

