- Print
- PDF
Create and Configure Lasernet Environments
On each server that will host a Lasernet environment, you must use the Lasernet Service Manager to create the Lasernet environment. The tool will create a corresponding Windows service on that server.
You must also configure the new Lasernet environment.
Steps
To create a Lasernet environment on a server and configure it, follow the quick start process or the full installation and setup process on this page.
Note
About the quick start process: The quick start process is a simpler route to an operational Lasernet system and it requires only basic IT knowledge. However, it results in a system that is suitable only for demonstration or trial purposes. For more information about the quick start process (and its inherent compromises), see the main Lasernet 11 Installation and Setup Guide page.
About the full installation and setup process: The full installation and setup process describes all available installation and setup options and is suitable for setting up production Lasernet systems. However, parts of it require some IT and database administration knowledge.
Quick Start Installation Process
In the Windows Start menu, click Lasernet 11 > Lasernet Service Manager 11. The Lasernet Service Manager 11 window opens.
Create a Lasernet environment on the server:
In the Lasernet Service Manager 11 window, click Add (see 1 in the image below).
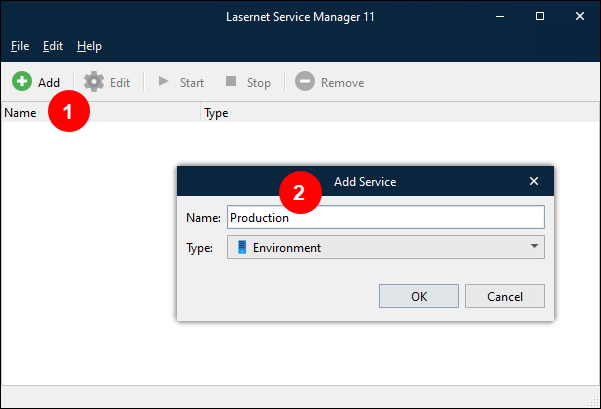
Enter the Name (2) of the new environment. Make a note of the name that you enter. The image above contains Production as the name, but you can use any name for the Lasernet environment in your Lasernet system; as a suggestion, enter Lasernet as the Name.
Ensure that Environment is selected in the Type dropdown list.
Click OK. A window that contains the default configuration for the new environment opens.
Click Ok to close the window and accept the default configuration.
In the Lasernet Service Manager 11 window, select the new environment and click Start in the toolbar. The Lasernet environment is now running.
.png)
Next Steps
After creating Lasernet environments, the next step of the Lasernet 11 installation and setup process is to configure the Lasernet Config service.
Full Installation and Setup Process
In the Windows Start menu, click Lasernet 11 > Lasernet Service Manager 11. The Lasernet Service Manager 11 window opens.
Create a Lasernet environment on the server:
In the Lasernet Service Manager 11 window, click Add (see 1 in the image below).

Enter the Name (2) of the new environment.
Ensure that Environment is selected in the Type dropdown list.
Click OK. A window that contains the default configuration for the new environment opens.
In the new window, check the environment’s default configuration and modify it (if necessary):
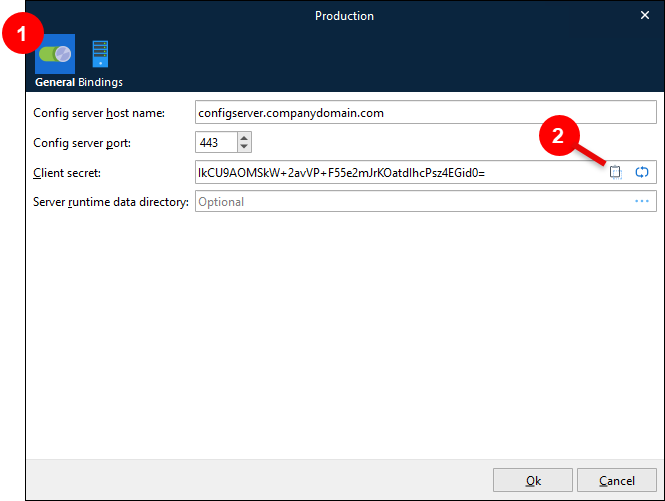
On the General tab (see 1 in the image below), ensure that Config server host name and Config server port are correct. If these are incorrect, the environment will be unable to communicate with Lasernet Config Server.
Note
You configure Lasernet Config Server during the next stage of this installation and deployment process. As a result, you would not have opened the Properties window for Lasernet Config Server and configured its port number yet.
However, the default Config server port number (443) matches the port number that Lasernet Config Server is configured to use by default. In most situations, this is satisfactory. You would need to change this port number (in the Lasernet Config Server and environment’s configurations) only if necessary to prevent port clashes with other software running on the same server.
The default Config server host name of localhost is appropriate if Lasernet Config Server is running on the same server as this environment. If Lasernet Config Server is running on another server, enter that server’s hostname with a fully-qualified domain name.
If you later find that Config server host name and Config server port are incorrect in this environment’s configuration, click this environment in the Lasernet Service Manager 11 window, click Edit, and then update Config server host name and Config server port.
Lasernet Service Manager generates a Client secret for the environment. Make a note of this code as you might need it when you configure Lasernet Config Server.
Tip
You can click Copy to clipboard (2).
Tip
To generate a different client secret, click the adjacent Generate (looping arrows) button.
Optional: If you leave the Server runtime data directory box blank, the environment will use the default location for storing configuration files, log files, and temporary files for that environment. In most situations, this local file location is satisfactory. If you want to specify where the environment stores this data, enter or select a directory.
Tip
For faster processing, use a local file location rather than a network location. Ensure that the location is not user-specific (for example, do not use the Windows Desktop).
Configure the environment’s port number:
Click the Bindings tab (see 1 in the image below).
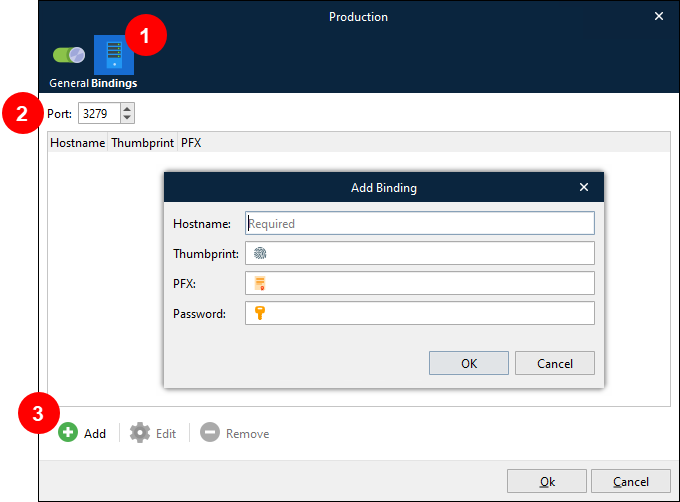
If necessary, modify the Port number (2).
Note
Modify the port number only if necessary to prevent port clashes with other software running on the same server (including Lasernet itself).
For example, if a server hosts multiple Lasernet environments, each environment must have a unique Port number.
If necessary, specify the hostnames to bind a local server certificate to. The environment will use the certificate to prove the server’s identity; the certificate also provides encryption keys to secure communication between server and client. An environment can use certificates installed in the Windows certificate store (in the Computer certificates area) or certificates stored on disk as PFX files. You must create a binding for every hostname that clients will use to connect to the environment.
Note
If no bindings are configured, Lasernet will autogenerate self-signed certificates for
localhost,<server name>and the server’s fully qualified domain name (FQDN).To specify a binding, follow these steps:
Click Add (3).
In the Add Binding window, enter a Hostname. This is the hostname that the certificate will be bound to. Valid values for Hostname are a hostname (without a domain specified), a FQDN, or an IP address.
Provide certificate details:
If Thumbprint is supplied, the certificate (in the Windows certificate store) with the specified thumbprint will be used.
PFX is the path and filename to a certificate (including private key) that is stored in PFX format. Password is the password for the PFX file.
If you leave both Thumbprint and PFX blank, a self-signed certificate for the specified Hostname will be generated and stored in the Windows Certificate Store.
Click OK to save the binding.
Note
Repeat these steps for every hostname that clients will use to connect to the environment. For example, some clients might connect to
localhost, whereas other clients might connect to the server’s FQDN. Multiple bindings can point to the same certificate, if necessary.Click Ok to close the environment properties window and save your configuration changes.
In the Lasernet Service Manager 11 window, select the new environment and click Start in the toolbar. The Lasernet environment is now running.
.png)
Firewall Configuration
If the Lasernet environment is not running on the same server as Lasernet Config Server, ensure that firewall configurations are modified to enable the environment and Lasernet Config Server to communicate with each other.
Next Steps
After creating Lasernet environments, the next step of the Lasernet 11 installation and setup process is to configure the Lasernet Config service.



